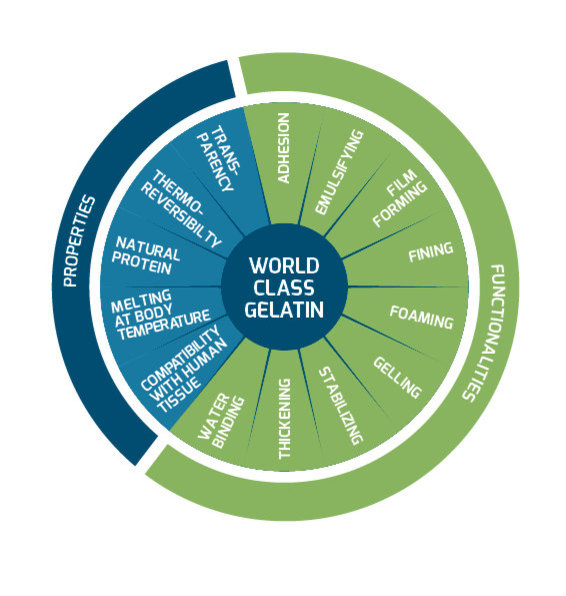
Rousselot® Gelatin is a multi-talented ingredient which helps make formulation easier and foster innovation. Its gelling, foaming, emulsifying and binding functionalities are complemented by numerous characteristics that make it irreplaceable in many applications, either in the pharmaceutical, food or nutrition industries.
Gelling
What makes gelatin really unique in terms of functionality is its thermo-reversible gelling power. A gelatin-based formulation gels when cooled and liquefies when re-heated. This transformation occurs rapidly and can be repeated without major changes in characteristics. A specific characteristic of gelatin is its so-called bloom. The bloom value specifies the gelling strength of gelatin. We offer gelatins with bloom values ranging from 75 to 300.
Gelatin melts at around body temperature. In food products, the result is an excellent mouthfeel as well as intensive flavor release. These properties make gelatin perfect for gummies and marshmallows, but also for other applications, such as pharma capsules.
Foaming
Foaming is the process in which a mass of small bubbles forms in a liquid or a solid. This is also known as a colloidal dispersion of a gas in a liquid or solid medium.
Film forming
Film forming is the process that converts either a liquid solution or a liquid dispersion into a thin, pliable, cohesive, and continuous (semi) dry sheet of the dissolved or dispersed material, called a film. This functionality is used in the manufacturing of capsules and microcapsules. It is also used in coating, for example, in confectionery.
Thickening
Texture refers to the consistency of the final product. Gelatin can help formulators achieve the desired texture, making a product softer or harder.
Water-binding
Our gelatins can bind water, thereby preserving the integrity of your product. This is linked to the affinity of gelatin for water. Gelatin swells and binds up to 10 times its weight in water. This water retention capacity helps prevent exudation and consequent syneresis, for example, in dairy applications. It also makes gelatin the choice ingredient in low-fat or reduced-fat foods, in which part of the fat is replaced by water.
Emulsifying
Emulsifying is the process that converts two (at least partly) immiscible liquids – usually oil and water – into a dispersion of droplets of one liquid into the other.
Stabilizing
Gelatin’s physicochemical properties, and its concentration in the final application, create a perfectly stable system that can significantly extend the shelf-life of the product in question.
Adhesion
Gelatin allows ingredients or components to stick together, whatever the application.
Fining
Fining, or clarifying, involves the formation of a floccular precipitate in beverages that will absorb the natural haze-forming constituents while settling.
