What is gelatin
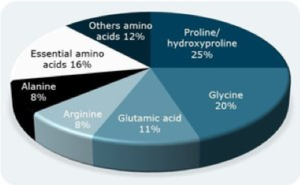
Gelatin is a protein and hydrocolloid that is obtained by partial hydrolysis of raw collagen, a substance found in high concentrations in animal skins and bones. It is a natural and pure protein, typically consisting of 85% protein, 13% water and 2% minerals at a caloric value of 370 kcal per 100g. It is easily and fully digestible, providing consumers with eight of the nine essential amino acids needed by the human body. In total, gelatin contains 18 different amino-acids and is particularly rich in glycine, proline and hydroxyproline. Together, these represent almost 50% of a gelatin molecule’s composition. Hydroxyproline is an amino-acid specific to gelatin.
Designed by nature
Gelatin is classified as a foodstuff – not a food additive - and has received GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) status from the United States’ Food and Drug Administration (USFDA). Gelatin has no e-numbers, is non-allergenic and is free of cholesterol, purine and fat. It qualifies worldwide as a key ingredient for achieving clean labelling.
Highly versatile and multifunctional
Successfully used in food and pharma applications for many centuries, gelatin offers more functionalities than any other hydrocolloids making it an unrivalled asset in formulation design. In fact, gelatin is often used to replace several mono-functional hydrocolloids in a single application, thereby simplifying formulation and contributing to simpler, more transparent labeling.
Read more on the functionalities of gelatin
Rousselot world-class gelatins
As the world’s leading producer of gelatin and collagen-based solutions, we offer world-class products of consistent, premium quality and high diversity.
A pure protein
- Gelatin is a protein and a food ingredient
- It has no e-number and is a key ingredient for achieving clear labelling
- Gelatin is also non-allergenic, cholesterol free, purine-free and fat-free
- Gelatin is a totally digestible protein and contains 4 kcal/g

